|
Home
CV
Publications
Principles
Software
Contacts
en ru
|
Dispersive area
|
|

|
Dispersive
area (DA) is an
area of a closed figure formed by a contour segment AB at a given
point P of the topographic surface and two flow lines l3
and l4 going down slope from the contour segment ends*. The unit of measurement is m2.
Dispersive area measures a
downslope area potentially exposed by flows passing through the given point
on the topographic surface.
Like
other nonlocal morphometric variables, dispersive area can be derived
from a digital elevation model (DEM) by flow
routing algorithms.
|
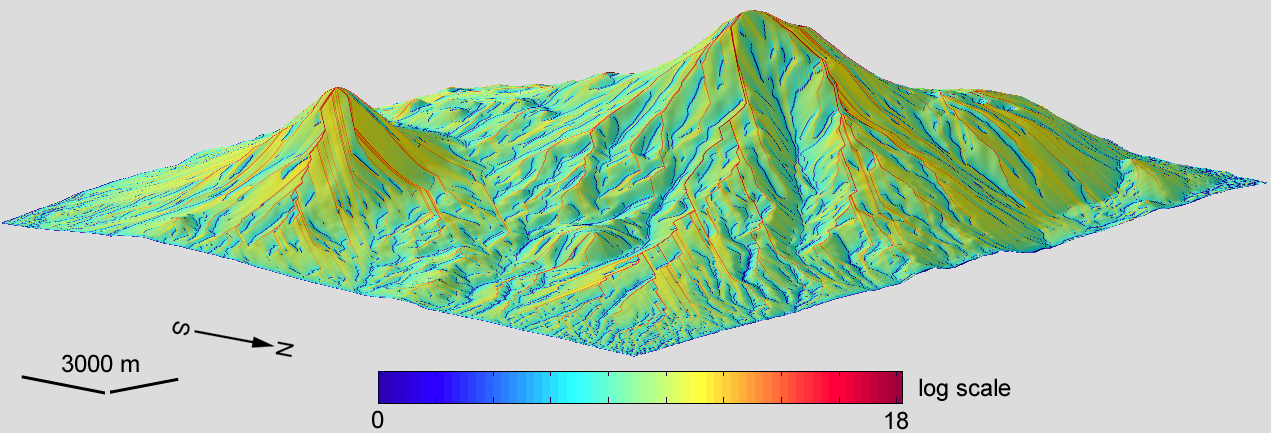
Example**.
A model of dispersive area was derived from a DEM of
Mount Ararat by the
Martz–de Jong method adapted to spheroidal equal angular grids. The model includes 779,401 points (the matrix 1081 x 721); the
grid spacing is 1". To deal with the large
dynamic range of this variable, its
values were logarithmically transformed.
The vertical exaggeration of the 3D model is 2x. The data processing and modelling were carried out using the software Matlab R2008b and LandLord 4.0.
References
* Speight,
J.G., 1974. A parametric approach to landform regions. Progress in
Geomorphology: Papers in Honour of D.L. Linton. London: Institute of
British Geographers, pp. 213–230.
** Florinsky,
I.V., 2017. An illustrated introduction to
general geomorphometry. Progress in Physical Geography, 41:
723–752. doi pdf
For
details and other examples, see:
|

|
DIGITAL TERRAIN ANALYSIS
IN SOIL SCIENCE AND GEOLOGY
2nd revised edition
I.V. Florinsky
Elsevier / Academic Press, 2016
Amsterdam, 486 p.
ISBN 978-0-12-804632-6
Contents Summary
ScienceDirect
|
|


